By: Team W10-2 Since: AUG 2018 Licence: MIT
- 1. Setting up
- 2. Design
- 3. Implementation
- 3.1. Storage Component Design
- 3.2. Write Review Feature
- 3.3. Sign Up, Login and Logout Feature
- 3.4. Adding, accepting and deleting friends and friend requests
- 3.5. Payment Splitting Feature
- 3.6. Internal Representation of Dates
- 3.7. Jio Feature
- 3.8. User Schedule Feature
- 3.9. Logging
- 3.10. Configuration
- 4. Documentation
- 5. Testing
- 6. Dev Ops
- Appendix A: Suggested Programming Tasks to Get Started
- Appendix B: Product Scope
- Appendix C: User Stories
- Appendix D: Use Cases
- Appendix E: Non Functional Requirements
- Appendix F: Glossary
- Appendix G: Instructions for Manual Testing
- G.1. Launch and Shutdown
- G.2. Login a User
- G.3. Log Out a User
- G.4. Display Current User Profile
- G.5. Write a Review
- G.6. Saving data
- G.7. Adding friends
- G.8. Accepting friends
- G.9. Deleting friend requests
- G.10. Deleting friends
- G.11. Adding groups
- G.12. Accepting groups
- G.13. Adding members to groups
- G.14. Deleting group requests
- G.15. Deleting group
- G.16. Create a jio
- G.17. Join a jio
- G.18. Delete jio
- G.19. Block Date from your schedule.
- G.20. Free Date from your schedule.
- G.21. List your schedule for the week.
- G.22. Find free timeslots to meet among your group members for a week.
- G.23. Add Debt
- G.24. Add Group Debt
- G.25. Accept Debt Request
- G.26. Delete Debt Request
- G.27. Clear Debt
1. Setting up
1.1. Prerequisites
-
JDK
9or laterJDK 10on Windows will fail to run tests in headless mode due to a JavaFX bug. Windows developers are highly recommended to use JDK9. -
IntelliJ IDE
IntelliJ by default has Gradle and JavaFx plugins installed.
Do not disable them. If you have disabled them, go toFile>Settings>Pluginsto re-enable them.
1.2. Setting up the project in your computer
-
Fork this repo, and clone the fork to your computer
-
Open IntelliJ (if you are not in the welcome screen, click
File>Close Projectto close the existing project dialog first) -
Set up the correct JDK version for Gradle
-
Click
Configure>Project Defaults>Project Structure -
Click
New…and find the directory of the JDK
-
-
Click
Import Project -
Locate the
build.gradlefile and select it. ClickOK -
Click
Open as Project -
Click
OKto accept the default settings -
Open a console and run the command
gradlew processResources(Mac/Linux:./gradlew processResources). It should finish with theBUILD SUCCESSFULmessage.
This will generate all resources required by the application and tests. -
Open
XmlAdaptedPerson.javaandMainWindow.javaand check for any code errors-
Due to an ongoing issue with some of the newer versions of IntelliJ, code errors may be detected even if the project can be built and run successfully
-
To resolve this, place your cursor over any of the code section highlighted in red. Press ALT+ENTER, and select
Add '--add-modules=…' to module compiler optionsfor each error
-
-
Repeat this for the test folder as well (e.g. check
XmlUtilTest.javaandHelpWindowTest.javafor code errors, and if so, resolve it the same way)
1.3. Verifying the setup
-
Run the
seedu.address.MainAppand try a few commands -
Run the tests to ensure they all pass.
1.4. Configurations to do before writing code
1.4.1. Configuring the coding style
This project follows oss-generic coding standards. IntelliJ’s default style is mostly compliant with ours but it uses a different import order from ours. To rectify,
-
Go to
File>Settings…(Windows/Linux), orIntelliJ IDEA>Preferences…(macOS) -
Select
Editor>Code Style>Java -
Click on the
Importstab to set the order-
For
Class count to use import with '*'andNames count to use static import with '*': Set to999to prevent IntelliJ from contracting the import statements -
For
Import Layout: The order isimport static all other imports,import java.*,import javax.*,import org.*,import com.*,import all other imports. Add a<blank line>between eachimport
-
Optionally, you can follow the UsingCheckstyle.adoc document to configure Intellij to check style-compliance as you write code.
1.4.2. Updating documentation to match your fork
After forking the repo, the documentation will still have the SE-EDU branding and refer to the se-edu/addressbook-level4 repo.
If you plan to develop this fork as a separate product (i.e. instead of contributing to se-edu/addressbook-level4), you should do the following:
-
Configure the site-wide documentation settings in
build.gradle, such as thesite-name, to suit your own project. -
Replace the URL in the attribute
repoURLinDeveloperGuide.adocandUserGuide.adocwith the URL of your fork.
1.4.3. Setting up CI
Set up Travis to perform Continuous Integration (CI) for your fork. See UsingTravis.adoc to learn how to set it up.
After setting up Travis, you can optionally set up coverage reporting for your team fork (see UsingCoveralls.adoc).
| Coverage reporting could be useful for a team repository that hosts the final version but it is not that useful for your restaurantal fork. |
Optionally, you can set up AppVeyor as a second CI (see UsingAppVeyor.adoc).
| Having both Travis and AppVeyor ensures your App works on both Unix-based platforms and Windows-based platforms (Travis is Unix-based and AppVeyor is Windows-based) |
1.4.4. Getting started with coding
When you are ready to start coding,
-
Get some sense of the overall design by reading Section 2.1, “Architecture”.
-
Take a look at Appendix A, Suggested Programming Tasks to Get Started.
2. Design
2.1. Architecture
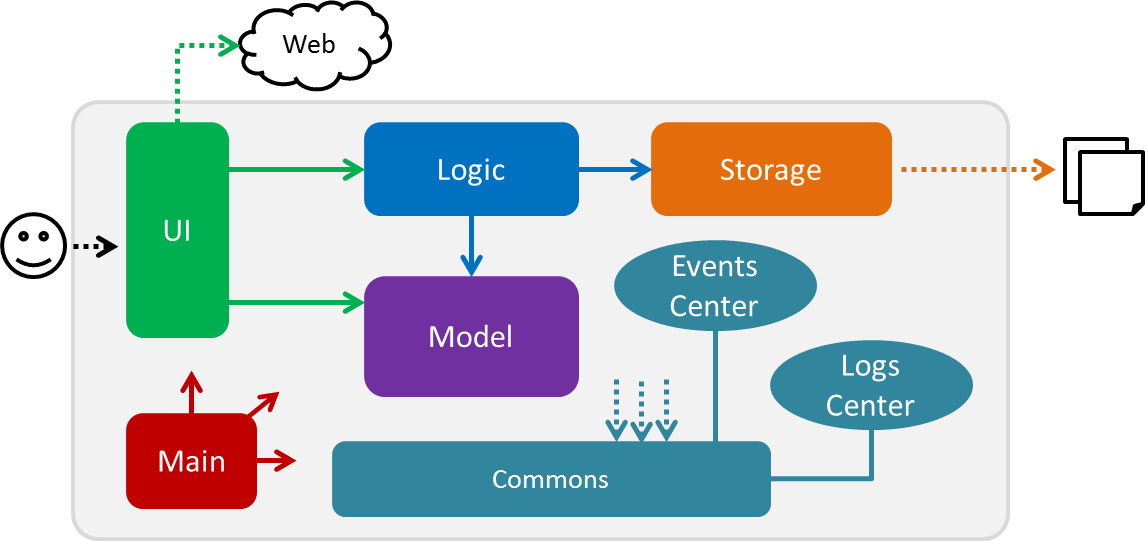
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the App. Given below is a quick overview of each component.
The .pptx files used to create diagrams in this document can be found in the diagrams folder. To update a diagram, modify the diagram in the pptx file, select the objects of the diagram, and choose Save as picture.
|
Main has only one class called MainApp. It is responsible for,
-
At app launch: Initializes the components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
-
At shut down: Shuts down the components and invokes cleanup method where necessary.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components. Two of those classes play important roles at the architecture level.
-
EventsCenter: This class (written using Google’s Event Bus library) is used by components to communicate with other components using events (i.e. a form of Event Driven design) -
LogsCenter: Used by many classes to write log messages to the App’s log file.
The rest of the App consists of four components.
Each of the four components
-
Defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. -
Exposes its functionality using a
{Component Name}Managerclass.
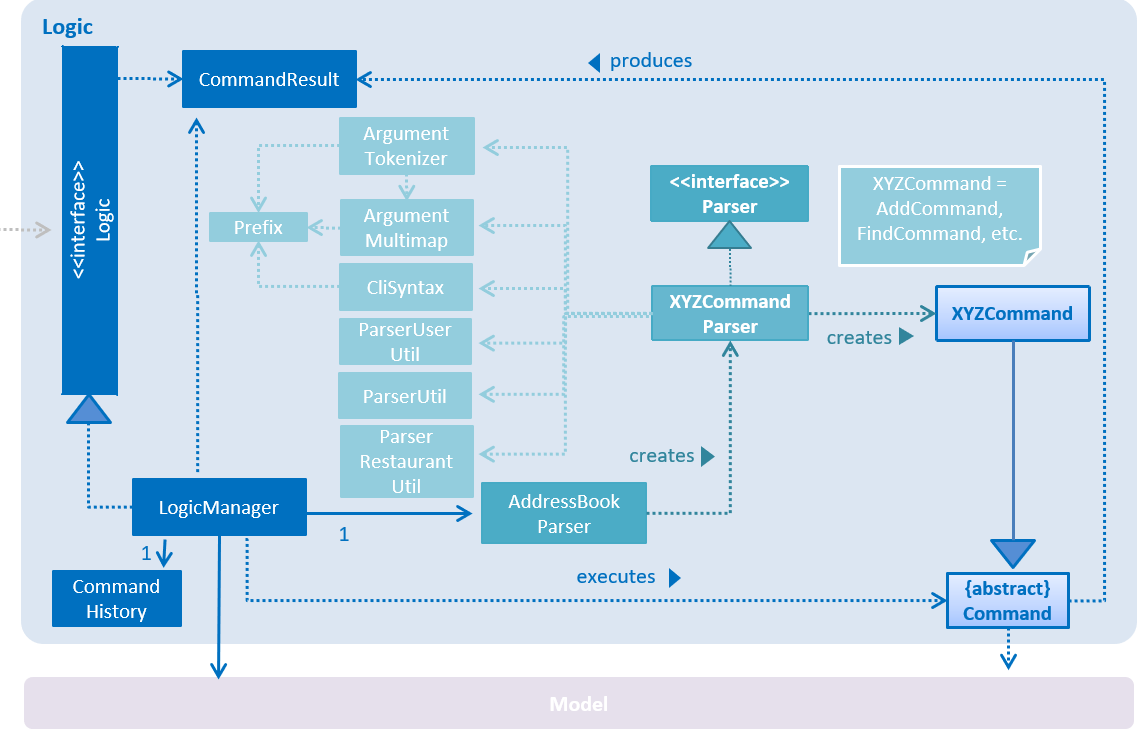
For example, the Logic component (see the class diagram given below) defines it’s API in the Logic.java interface and exposes its functionality using the LogicManager.java class.
Events-Driven nature of the design
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact for the scenario where the user issues the command delete 1.
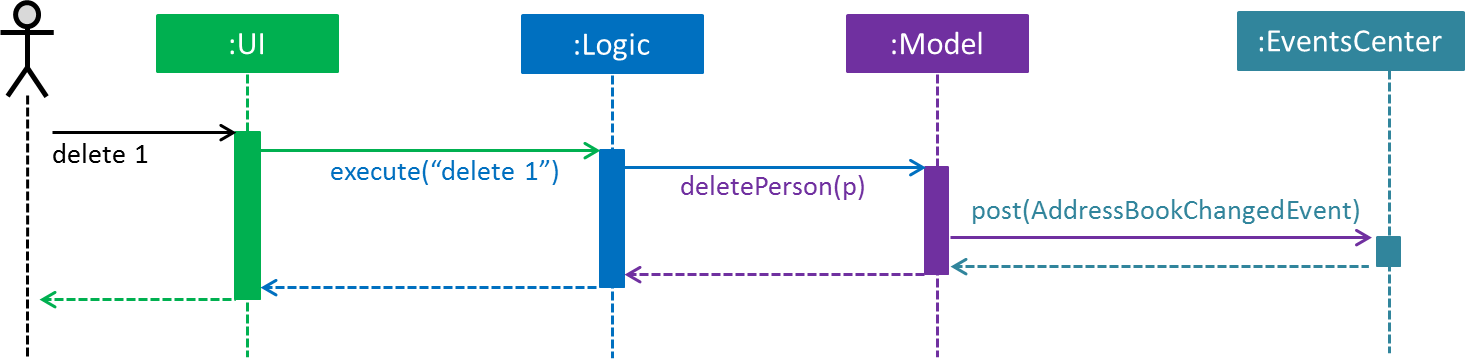
delete 1 command (part 1)
Note how the Model simply raises a AddressBookChangedEvent when the Address Book data are changed, instead of asking the Storage to save the updates to the hard disk.
|
The diagram below shows how the EventsCenter reacts to that event, which eventually results in the updates being saved to the hard disk and the status bar of the UI being updated to reflect the 'Last Updated' time.
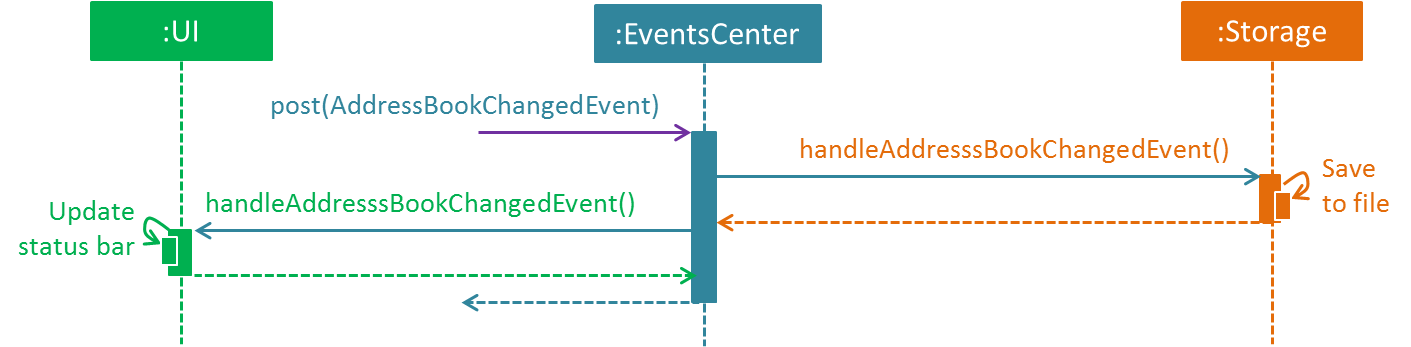
delete 1 command (part 2)
Note how the event is propagated through the EventsCenter to the Storage and UI without Model having to be coupled to either of them. This is an example of how this Event Driven approach helps us reduce direct coupling between components.
|
The sections below give more details of each component.
2.2. UI component
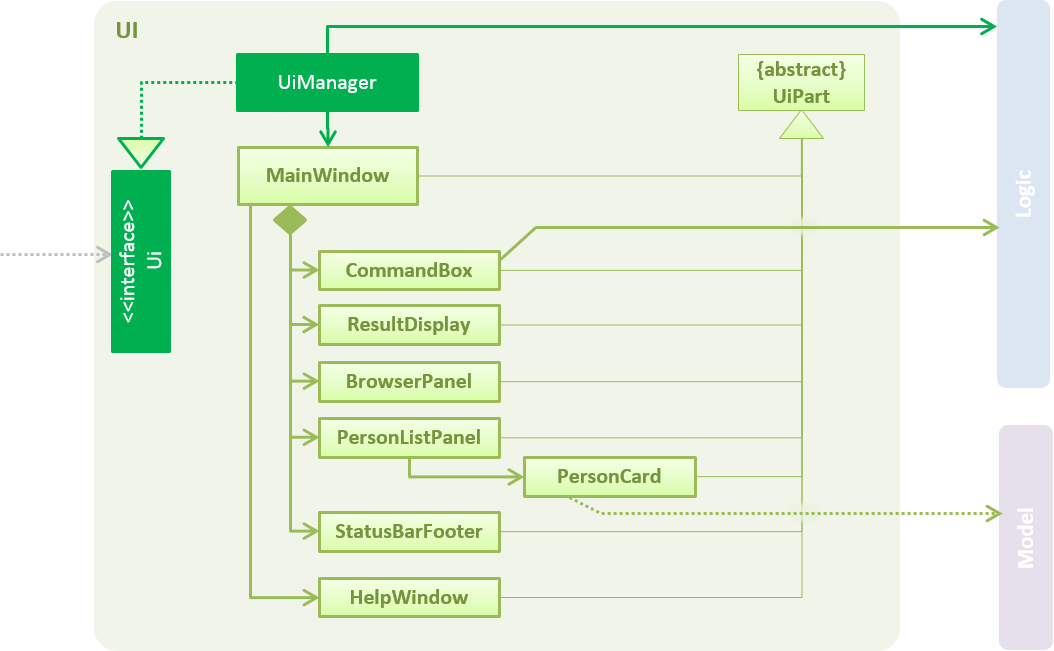
API : Ui.java
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts e.g.CommandBox, ResultDisplay, RestaurantListPanel, StatusBarFooter, BrowserPanel etc. All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class.
The UI component uses JavaFx UI framework. The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder. For example, the layout of the MainWindow is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
-
Executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. -
Binds itself to some data in the
Modelso that the UI can auto-update when data in theModelchange. -
Responds to events raised from various parts of the App and updates the UI accordingly.
2.3. Logic component

API :
Logic.java
-
Logicuses theAddressBookParserclass to parse the user command. -
This results in a
Commandobject which is executed by theLogicManager. -
The command execution can affect the
Model(e.g. adding a restaurant) and/or raise events. -
The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is passed back to theUi.
Given below is the Sequence Diagram for interactions within the Logic component for the execute("delete 1") API call.
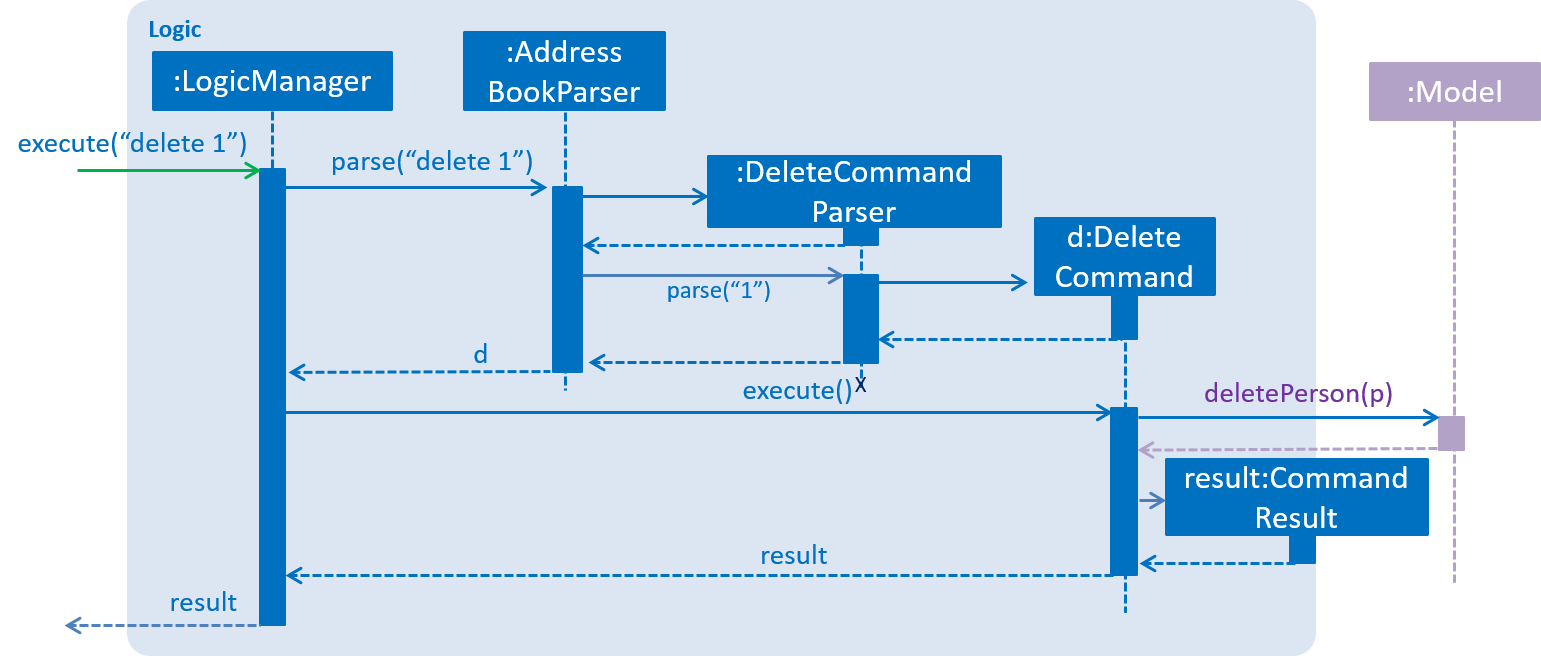
delete 1 Command2.4. Model component
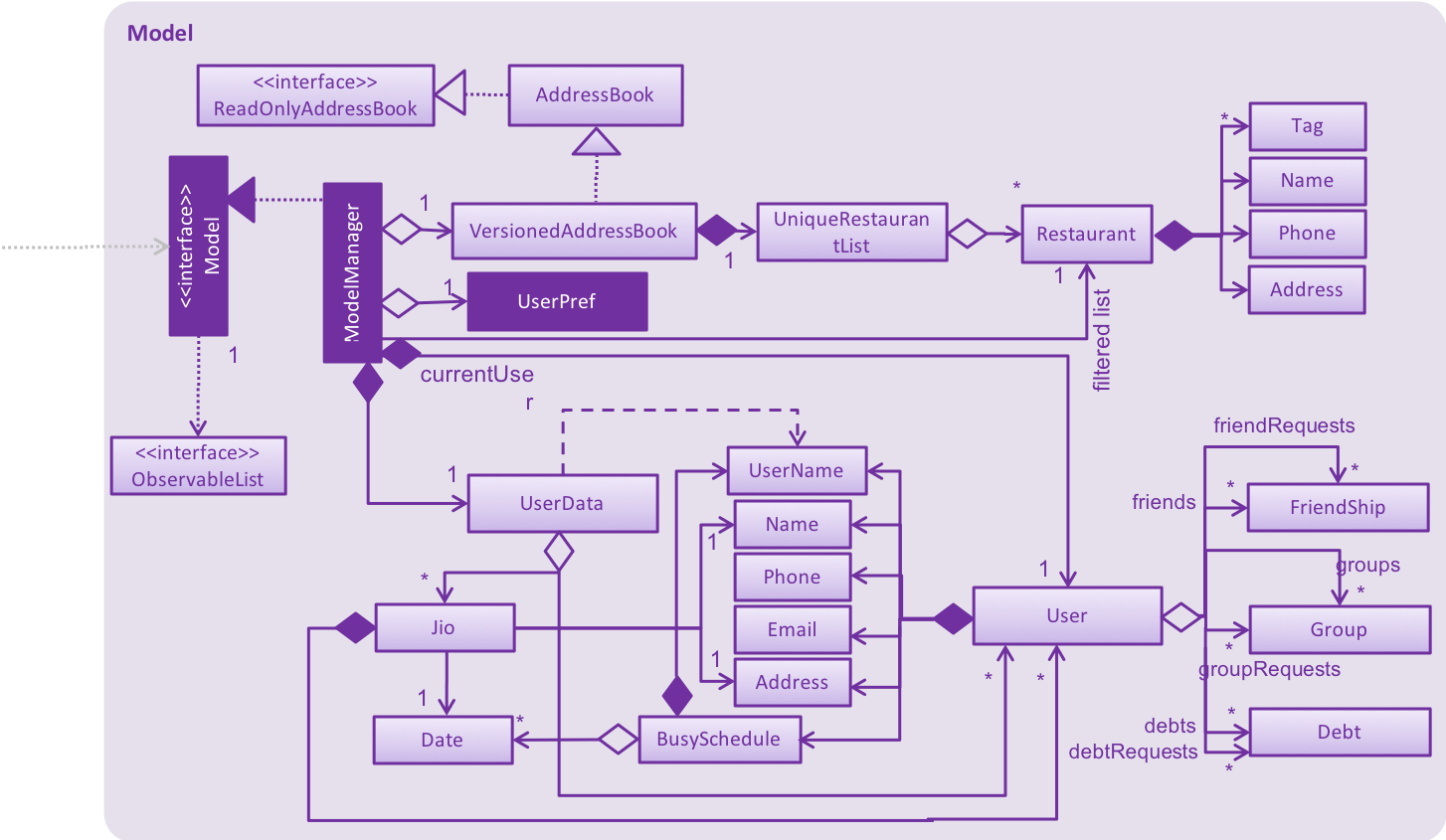
API : Model.java
The Model,
-
stores a
UserPrefobject that represents the user’s preferences. -
stores the Address Book data.
-
exposes an unmodifiable
ObservableList<Restaurant>that can be 'observed' e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list change. -
does not depend on any of the other three components.
2.5. Storage component
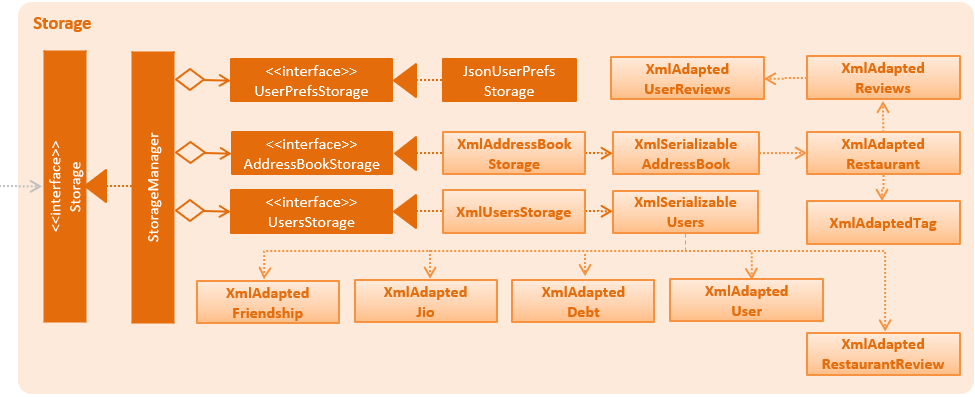
API : Storage.java
The Storage component,
-
can save
UserPrefobjects in json format and read it back. -
can save the Address Book data in xml format and read it back.
-
can save the User data in xml format and read it back.
2.6. Common classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the seedu.addressbook.commons package.
3. Implementation
This section describes some noteworthy details on how certain components and features are implemented.
3.1. Storage Component Design
3.1.1. Current Implementation
The storage of Makan book is split into two different xml files namely users.xml and addressbook.xml where data
relating to users are stored in the formal and data relating to restaurants are stored in the latter.
Aspect: Ease of Maintenance
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Split Storage into into two different components.
-
Dividing storage into two different components meant the creation of multiple other classes for the storing of data relating to users such as
UserDataandXmlSerializableUsers. -
However, this was deemed necessary and appropriate as User and Restaurant is abstracted out and encapsulated. Should there be a reset of Users, the restaurant data would remain unaffected.
-
Pros: Abstraction of Data that are separate.
-
Pros: Easier to maintain.
-
Cons: Time costs to implement.
-
-
Alternative 2: Storing the data of Users and Restaurants in the same
addressbook.xmlfile.-
Pros: Easier to implement.
-
Cons: Difficult to maintain and scale. All sorts of data relating to users will be stored together with restaurants.
-
3.2. Write Review Feature
3.2.1. Current Implementation
The write review feature allows a user to write a review about a restaurant. This review is available for all users in the Makan Book to view. This review is then stored internally into the restaurant addressbook and the current user. When the command writeReview is called and executed, the model manager creates an UserReview (to be stored in restaurant addressbook) and a RestaurantReview (to be stored into User) as seen in the sequence diagram below.
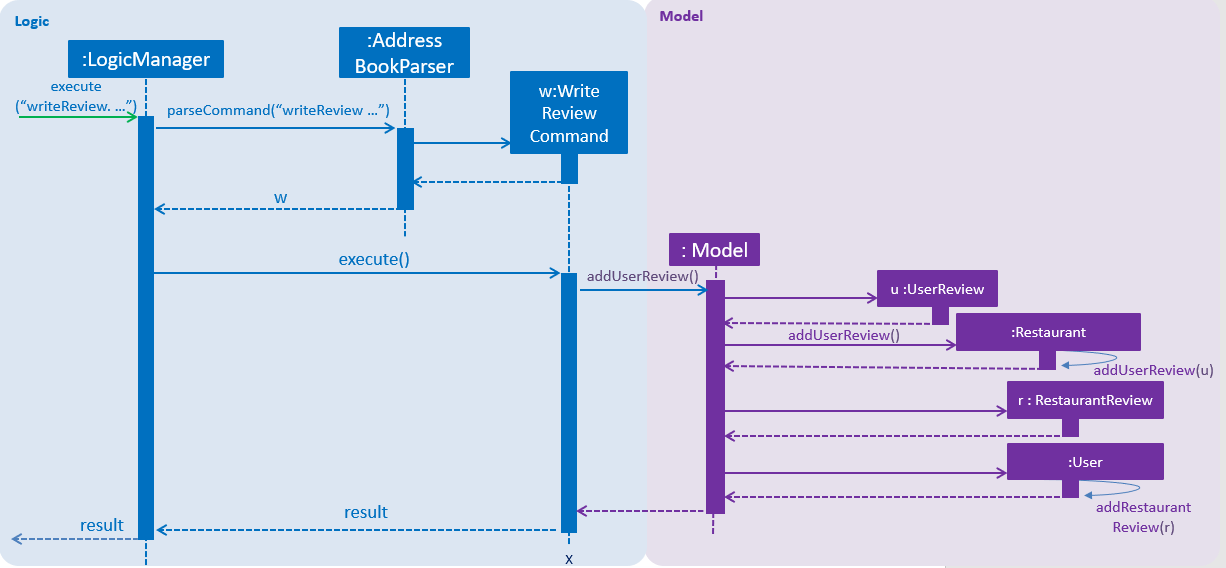
Additionally, a restaurant contains an overall rating, the average rating of all the reviews it has. The activity diagram below describes the process of updating the restaurant’s overall rating.
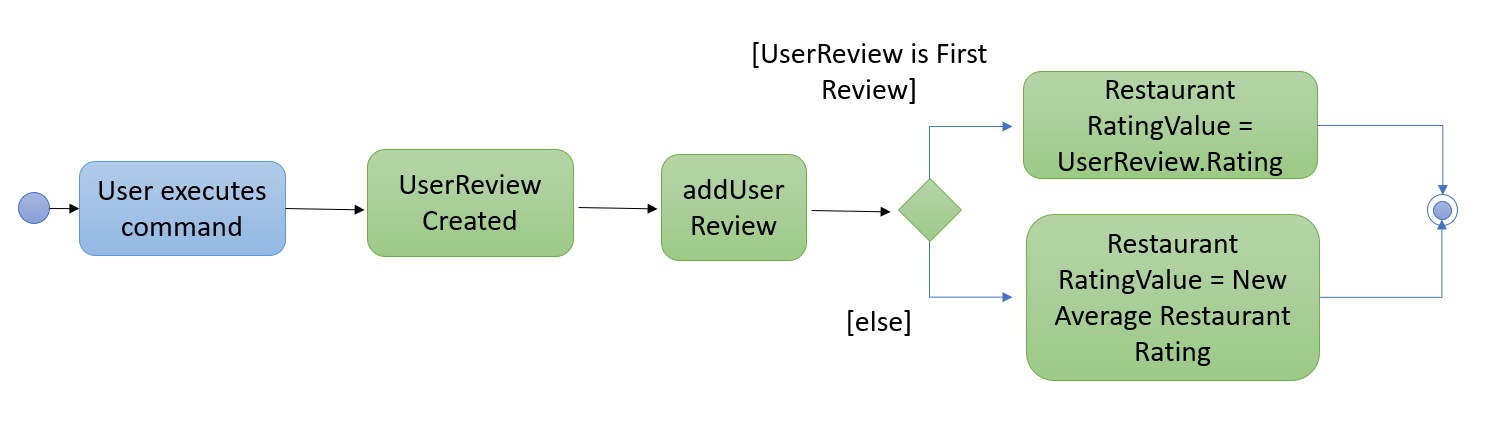
3.2.2. Design Considerations
Aspect: Where to store User Review
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Saves the review in both User and restaurant addressbook.
-
Pros: Greater abstraction and encapsulation of Data
-
Pros: Ease of displaying the list of reviews that a specific User has written
-
Pros: Ease of displaying the list of reviews of a specific Restaurant
-
Pros: Ease of updating the Overall Rating of a Restaurant
-
Cons: Contains a number of repeated code.
-
E.g. UserReview and RestaurantReview are identical except that UserReview stores the Restaurant Name while RestaurantReview stores the Username of the User.
-
-
-
Alternative 2: Saves the review in restaurant adddressbook.
-
Pros: Ease of Implementation (Significantly fewer classes)
-
Cons: Cluttered Storage of Data making it difficult to maintain and scale
-
3.3. Sign Up, Login and Logout Feature
3.3.1. Current Implementation
The current implementation of Makan Book does not allow the usage of all the features. Certain features require registration
or login of an account. For instance, the adding of friends can only be done upon log in. Sign Up, Login and Logout commands
can be entered through the Command Line Interface. The implementation is aided by the current modelManager which keeps track
of whether a user is currently signed in and which user it is. In doing so, data relating to this particular user during his session
can be saved.
3.4. Adding, accepting and deleting friends and friend requests
3.4.1. Current Implementation for Friendships
Friendships can have two statuses - ACCEPTED and PENDING. User A can send a friend request to User B which would then store a friendship with User A as PENDING under User B alone. User B can choose to accept or delete the friend request. If User chooses to delete the friend request, the PENDING friendship under User B will be deleted. If User B chooses to accept the friend request, the friendship status will be changed from PENDING to ACCEPTED for User B and an identical friendship will be added to User A, the one who initiated the friendship.
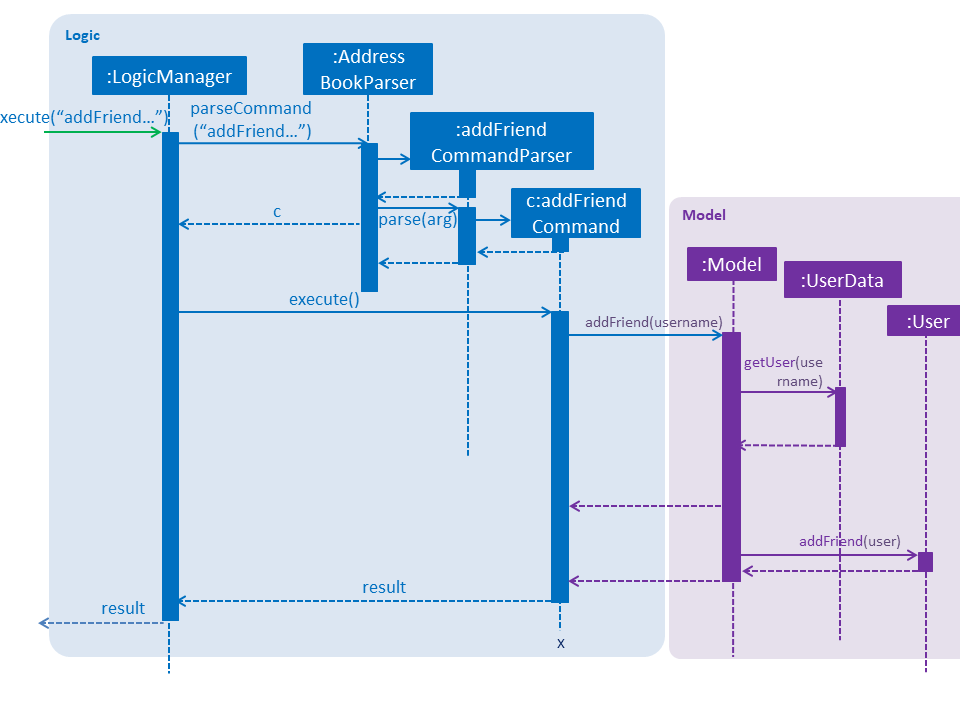
Now moving on to deletion of friends. Assuming that two Users C and D are friends with each other, and User C deletes his or her friendship with User D. This would delete the friendship stored under both User C and User D even if User D did not initiate the deletion of friendship. It is also possible to list the existing list of friends (ACCEPTED) and friend requests (PENDING).
The Friendship class itself stores 'me' (currently logged in User), 'friendUser' (other party in the friendship), 'friendshipStatus' (status of the friendship) and 'initiatedBy' (which party the friendship was initiated by). There is a restriction such that the 'initiatedBy' must be either 'me' or 'friendUser'. A friendship is immutable once created. Friendships are stored as an XML element under users.xml with the four attributes mentioned above.
3.4.2. Why the current implementation for Friendships
The PENDING friendships are only stored under the User who did not initiate the friendship. This so that when the listFriendRequests command is called so as to allow the User to accept and delete the friend requests accordingly, it only makes sense for the User to see the friendships that they wish to accept or delete (i.e. friendships not initiated by them). Thus, friend requests are only stored under the User who did not initiate the friendship.
There are two separate lists for friendships - one for friend requests and one for friends. This is to aid the listing functions and avoid confusion by simplifying the friendships stored under User.
Exceptions and why they are thrown
There are several exceptions thrown for the friendship commands. An exception is thrown for all friendship commands should there be no User logged in currently. Specifically for the adding of friends (i.e. sending friend requests) a User cannot send a request to himself. Moreover, if the User has previously sent a request which has yet to be accepted by the other User, the initiating User cannot send another request. However, if the recipient User has deleted the friend request, then the initiating User is able to send a new friend request. A blocking feature is to be made in v2.0. Moreover, a User cannot send a friend request to another User with whom they are already friends with.
When it comes to accepting friendships, there are several exceptions thrown too. If the User tries to accept a friend request not in their list of friend requests an exception is thrown. Similarly, an exception is thrown if the User tries to delete a friend request not in their list of friend requests or a friend who is not in their list of friends.
3.4.3. Alternatives considered for Friendships
For a while, I considered storing all friendships (both friend requests and friends) in the same list. However, I decided against this as this made things potentially confusing especially for a new developer coming in to retrieve only friends or friend requests.
XML storage
Initially, I faced a problem balancing making the code more OOP (to preserve the true spirit of software engineering) and storing friendships as an XML element. XML elements only take in Strings and not objects. However to store friendships, the elements stored include Users ('friendUser', 'me' and 'initiatedBy'). Thus, I considered sacrificing the OOP-nature of Friendships as proposed above and instead merely storing usernames as strings for the User.
To get around this problem, a hashmap mapping Username to the User is passed to the class doing the XML storage and loading of Friendships. Thus, OOP is not sacrificed as User is still the data type of the attributes stored in Friendship and Friendships can be created from the XML element with the aid of the hashmap.
Initially, I considered asking the initiating User to enter all the information about the other User to add them as a friend. This is so that I would be able to construct the User from the the information provided. However, this would be too inconvenient for the User and thus the hashmap mentioned before was used.
3.5. Payment Splitting Feature
3.5.1. Current Implementation
The payment splitting feature allow user to keep record for their debts, especially for gathering. Creditor can use
the addDebt to create a request to debtor, or addGroupDebt to create a request to all other members in a group.
A record of this debt will be made with a "pending" status and store to
both user.
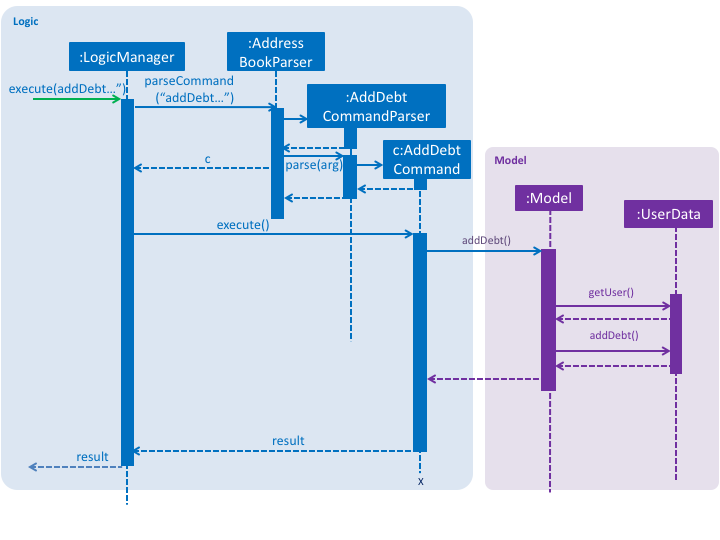
Debtor can then use the acceptDebtRequest to accept the request from creditor, which the status will be
changed to "accepted", or reject and delete the request by deleteDebtRequest, which the the debt record will be
deleted and removed from the storage. If the debt has been repaid, the creditor can use the clearDebt to mark the
debt as "cleared". Only the user who initialized the debt(creditor) can clear the debt, and only the other user(debtor)
can accept or delete the debt. An accepted debt needed to be confirmed by both users.
3.5.2. How the feature is implemented
The Debt class store creditor, debtor, amount, status and id(timestamp).
The creditor and debtor must be a user, amount should be larger than zero,
there are four status - PENDING, ACCEPTED, CLEARED and BALANCED and the id is a 15 digits long string to identify the debt.
Debts are stored as an XML element under users.xml with all the above attributes mentioned as a string.
3.5.3. Why it is implemented that way
The debt is under PENDING when it is created, it is treated as a request to the debtor. The debtor needs to accept
and make it to a ACCEPTED debt. The ACCEPTED debt need to be confirm by both side because we want to ensure its
accuracy. Also, only the user who initialize the debt(creditor) can clear the debt to prevent the debtor clear or delete
it for self benefit.
3.5.4. Alternatives considered.
Alternative 1: The debt can create by one user and do not need to be accepted
-
Pros:
-
Easy to store
-
Easy to mange
-
-
Cons:
-
Lost accuracy
-
Not fair to user
-
Alternative 2: The debt store separately instead of under user
-
Pros:
-
Easy to store
-
Easy to retrieve
-
Easy to implement
-
-
Cons:
-
Cannot achieve confirmation by user
-
It is cumbersome to user
-
3.6. Internal Representation of Dates
3.6.1. Current Implementation
Each date consists of three points of data: the NUS Week, the Day of the week, and the Time of the day. The dates are separated into 30 minute intervals as represented by the time. The time is stored in 24-hour format.
This implementation means that MakanBook is only tailored to work during the NUS semester. All features requiring some aspect of time will use this Date implementation.
3.6.2. Reasons for this implementation
Dates follow the NUS calendar to make it very intuitive for NUS students. Furthermore, this opens up ease of integrating with NUS mods in the future.
Time-intervals are set at 30 minutes to ease implementation and reduce storage needs.
3.6.3. Restrictions on usage of Date.
Dates are all limited to the NUS calendar, and no dates in the range of 0000 to 0600 hours can be created. The rational for this is to discourage improper sleeping hours among students in NUS – at least in that small window of time.
3.6.4. Alternatives considered
Another alternative considered was to use the Calendar library in Java to store the dates as an underlying data structure. However, as the NUS week system would be the most intuitive way of user input for students, this may only create additional work.
3.7. Jio Feature
3.7.1. Current Implementation
A Jio object stores information about the jio in the following objects: Name, Week, Day, Time, Address. The
Jio object also stores the people going on the jio as a list of Username. A Jio object cannot be modified after
creation, except to add a user (ie. append Username to the list). Jios are stored in the users.xml with each object
as an Xml element.
Creator (current user) is automatically added to the jio. If the group tag g/ is added, users under the group specified is retrieved from UserData and added to the jio.
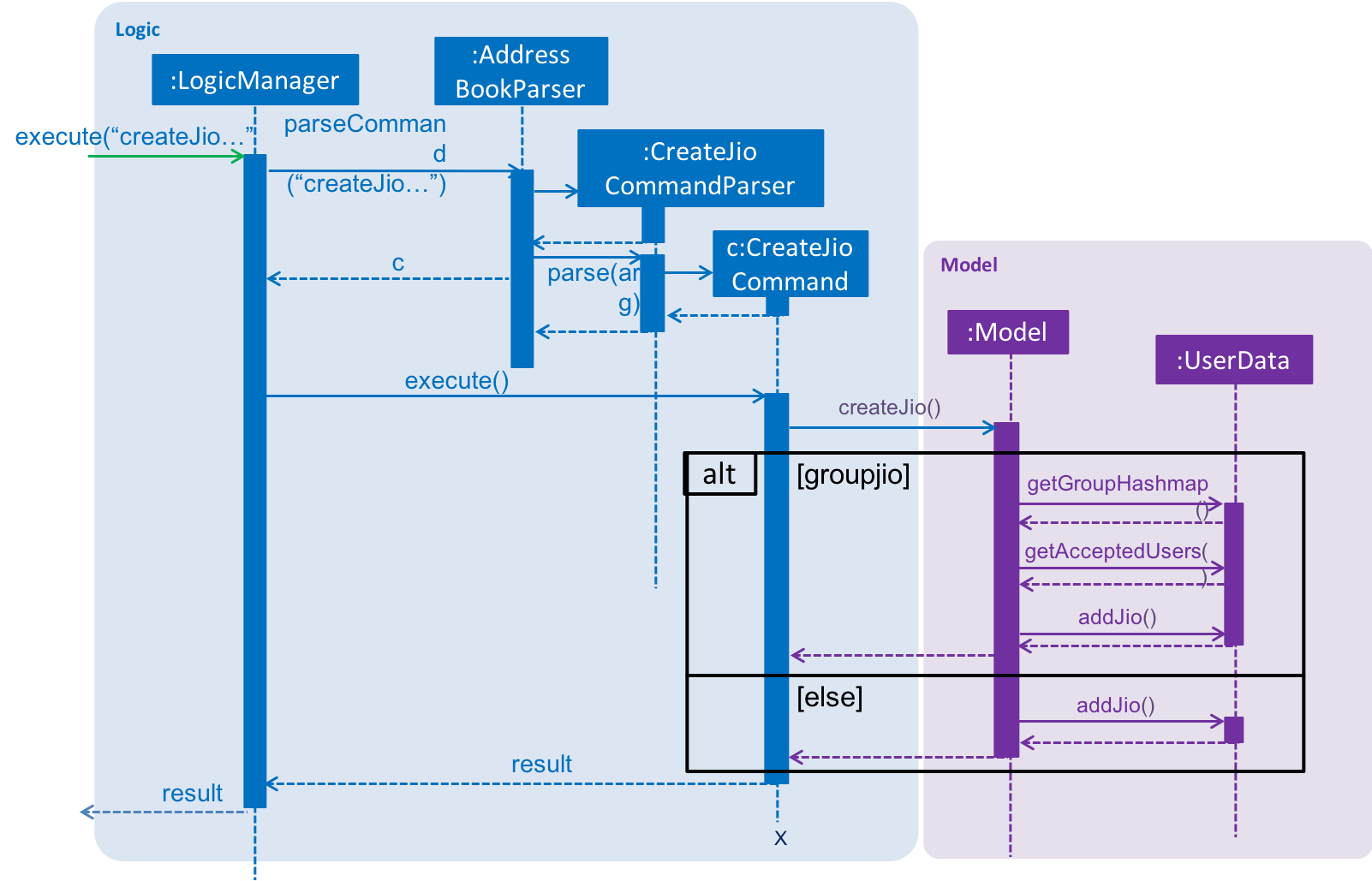
Jio-related Commands
createJio is implemented by creating a Jio object with the specified parameters, but an empty list of Username.
The Jio object is eventually passed to ModelManager, which adds the current user to the Jio and stores it in UserData.
Similarly, joinJio relies on ModelManager to add the current user to the jio. It also performs a check that the
user is not already in the list of Username, otherwise a CommandException is thrown.
All jio commands require the user to be logged in due to usage of current user, otherwise a NotLoggedInCommandException
is thrown. joinJio and deleteJio perform additional checks for whether the Jio exists, otherwise a CommandException
is thrown.
3.7.2. Reasons for this implementation
ModelManager exclusively handles all operations related to current user for encapsulation. Thus, the command classes
do not touch current user at all, but pass Jio objects on to ModelManager.
3.7.3. Alternatives Considered
Aspect: Storing jio
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Jios are stored separately.
-
Pros: Easy to implement.
-
Pros: Easy to retrieve jio from storage by searching for jio name.
-
Pros: Jio can listed easily.
-
Cons: Jio creator needs to be stored as an additional attribute if needed.
-
-
Alternative 2: Storing jios in User.
-
Pros: A jio can be identified by its creator
-
Cons: Difficult to list jios. Need to iterate through users.
-
Cons: Hard to retrieve a particular jio.
-
Aspect: Storing people going on jio
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): List of Username.
-
Pros: Easy to implement and list.
-
Cons: Users must have unique usernames.
-
-
Alternative 2: Storing a list of User instead.
-
Pros: All information about User is stored for possible retrieval in the future (eg. to view user timetables).
-
Cons: Difficult to store in Xml file. Users cannot easily be converted in to a single string.
-
Cons: May be storing unnecessary information.
-
3.8. User Schedule Feature
3.8.1. Benefits for the user
-
Any user using our MakanBook can add their schedules into their profile to block out dates that they are not free.
-
This way, any other person wanting to eat with other users can easily see which times they are free at.
-
To help the user arrange eating times with their groups, the user can also run the
findDatescommand to find common timeslots to eat at for groups.
3.8.2. Current Implementation
In MakanBook, we implemented a schedule feature according to the NUS Calendar: 17 weeks in a semester, with each day
split into 30 minute timeslots as mentioned above. Each timeslot is encapsulated by a Date object which contains the NUS Week, the Day of the week, and the Time that the 30 minute segment starts at.
A UniqueSchedule class is then used to encapsulate the list of busy timeslots for any individual user and UniqueSchedule contains two key pieces of information:
the Username to identify which user the schedule belongs to, and a HashMap that stores the list of busy Dates for
each corresponding NUS week.
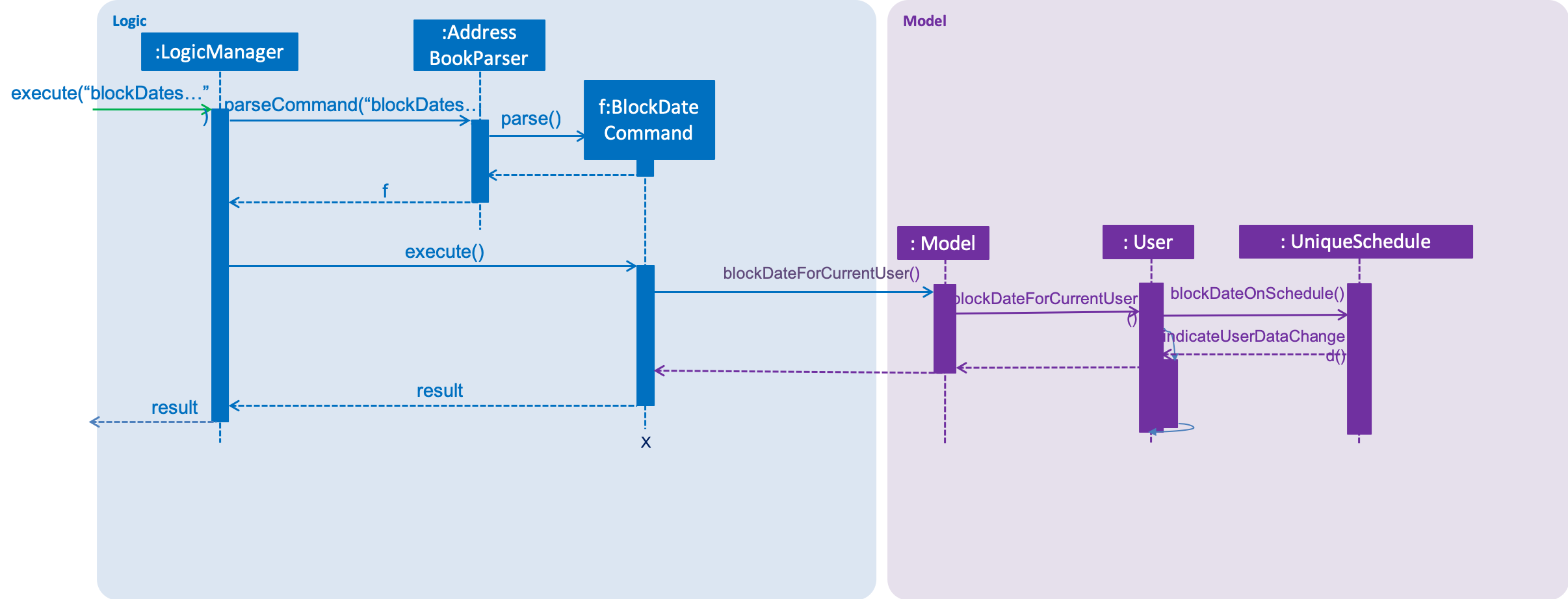
Storage of Timetable related Data
The entire user’s UniqueSchedule is stored in the users.xml file with each object as an XML element containing the username and all busy dates.
Algorithm for finding free timeslots to eat
Currently, each time listScheduleForUser or findDates is run, the system will retrieve the list of all unavailable dates for that NUS week.
Then, a complete list of free dates will be generated for that week. The list of blocked dates will be run against the complete free list, removing all blocked dates before the UI
receives the finalised list to display.
3.8.3. Reasons for this Implementation
All lists of dates are stored in a List instead of a Set. In the future, utilising Set may be a safer alternative to completely prevent the possibility of duplicates.
Currently, duplicate dates are checked through the contains method of List. Any programming violations are checked in the test suite.
Set data structures are not currently used as it will not interact well with the current XML storage system. For lack of time, this low-priority consideration will be set aside.
3.8.4. Timetable Commands
-
BlockDateCommandis specific to the logged in user, allowing the currentUserto save a date on his schedule where he is not free. ABlockDateCommandParseris used to parse the arguments necessary. -
FreeDateCommandis specific to the logged in user, allowing him to free up dates on his schedule. AFreeDateCommandParseris used to parse the arguments necessary. -
ListScheduleForWeekis specific to the logged in user. The command lists the user’s schedule for a given NUS week. A parser is necessary. -
FindDatesfinds common dates to eat between all users the group is in. The command lists all free timeslots to eat for a given NUS week, among the NUS group. A parser is necessary.
3.8.5. Restrictions on usage of Timetable commands
Timetable Commands can only be used when the User is logged into the MakanBook.
Exceptions are handled with the NotLoggedInCommandException class in the Logic component.
The algorithm for finding all the free dates for a user or group is found inside the UniqueSchedule class.
3.9. Logging
We are using java.util.logging package for logging. The LogsCenter class is used to manage the logging levels and logging destinations.
-
The logging level can be controlled using the
logLevelsetting in the configuration file (See Section 3.10, “Configuration”) -
The
Loggerfor a class can be obtained usingLogsCenter.getLogger(Class)which will log messages according to the specified logging level -
Currently log messages are output through:
Consoleand to a.logfile.
Logging Levels
-
SEVERE: Critical problem detected which may possibly cause the termination of the application -
WARNING: Can continue, but with caution -
INFO: Information showing the noteworthy actions by the App -
FINE: Details that is not usually noteworthy but may be useful in debugging e.g. print the actual list instead of just its size
3.10. Configuration
Certain properties of the application can be controlled (e.g App name, logging level) through the configuration file (default: config.json).
4. Documentation
We use asciidoc for writing documentation.
| We chose asciidoc over Markdown because asciidoc, although a bit more complex than Markdown, provides more flexibility in formatting. |
4.1. Editing Documentation
See UsingGradle.adoc to learn how to render .adoc files locally to preview the end result of your edits.
Alternatively, you can download the AsciiDoc plugin for IntelliJ, which allows you to preview the changes you have made to your .adoc files in real-time.
4.2. Publishing Documentation
See UsingTravis.adoc to learn how to deploy GitHub Pages using Travis.
4.3. Converting Documentation to PDF format
We use Google Chrome for converting documentation to PDF format, as Chrome’s PDF engine preserves hyperlinks used in webpages.
Here are the steps to convert the project documentation files to PDF format.
-
Follow the instructions in UsingGradle.adoc to convert the AsciiDoc files in the
docs/directory to HTML format. -
Go to your generated HTML files in the
build/docsfolder, right click on them and selectOpen with→Google Chrome. -
Within Chrome, click on the
Printoption in Chrome’s menu. -
Set the destination to
Save as PDF, then clickSaveto save a copy of the file in PDF format. For best results, use the settings indicated in the screenshot below.
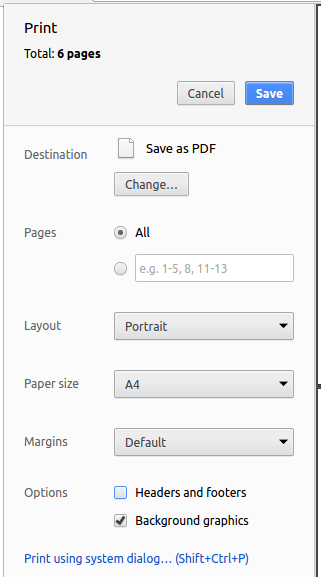
4.4. Site-wide Documentation Settings
The build.gradle file specifies some project-specific asciidoc attributes which affects how all documentation files within this project are rendered.
Attributes left unset in the build.gradle file will use their default value, if any.
|
| Attribute name | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
|
The name of the website. If set, the name will be displayed near the top of the page. |
not set |
|
URL to the site’s repository on GitHub. Setting this will add a "View on GitHub" link in the navigation bar. |
not set |
|
Define this attribute if the project is an official SE-EDU project. This will render the SE-EDU navigation bar at the top of the page, and add some SE-EDU-specific navigation items. |
not set |
4.5. Per-file Documentation Settings
Each .adoc file may also specify some file-specific asciidoc attributes which affects how the file is rendered.
Asciidoctor’s built-in attributes may be specified and used as well.
Attributes left unset in .adoc files will use their default value, if any.
|
| Attribute name | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
|
Site section that the document belongs to.
This will cause the associated item in the navigation bar to be highlighted.
One of: * Official SE-EDU projects only |
not set |
|
Set this attribute to remove the site navigation bar. |
not set |
4.6. Site Template
The files in docs/stylesheets are the CSS stylesheets of the site.
You can modify them to change some properties of the site’s design.
The files in docs/templates controls the rendering of .adoc files into HTML5.
These template files are written in a mixture of Ruby and Slim.
|
Modifying the template files in |
5. Testing
5.1. Running Tests
There are three ways to run tests.
| The most reliable way to run tests is the 3rd one. The first two methods might fail some GUI tests due to platform/resolution-specific idiosyncrasies. |
Method 1: Using IntelliJ JUnit test runner
-
To run all tests, right-click on the
src/test/javafolder and chooseRun 'All Tests' -
To run a subset of tests, you can right-click on a test package, test class, or a test and choose
Run 'ABC'
Method 2: Using Gradle
-
Open a console and run the command
gradlew clean allTests(Mac/Linux:./gradlew clean allTests)
| See UsingGradle.adoc for more info on how to run tests using Gradle. |
Method 3: Using Gradle (headless)
Thanks to the TestFX library we use, our GUI tests can be run in the headless mode. In the headless mode, GUI tests do not show up on the screen. That means the developer can do other things on the Computer while the tests are running.
To run tests in headless mode, open a console and run the command gradlew clean headless allTests (Mac/Linux: ./gradlew clean headless allTests)
5.2. Types of tests
We have two types of tests:
-
GUI Tests - These are tests involving the GUI. They include,
-
System Tests that test the entire App by simulating user actions on the GUI. These are in the
systemtestspackage. -
Unit tests that test the individual components. These are in
seedu.address.uipackage.
-
-
Non-GUI Tests - These are tests not involving the GUI. They include,
-
Unit tests targeting the lowest level methods/classes.
e.g.seedu.address.commons.StringUtilTest -
Integration tests that are checking the integration of multiple code units (those code units are assumed to be working).
e.g.seedu.address.storage.StorageManagerTest -
Hybrids of unit and integration tests. These test are checking multiple code units as well as how the are connected together.
e.g.seedu.address.logic.LogicManagerTest
-
5.3. Troubleshooting Testing
Problem: HelpWindowTest fails with a NullPointerException.
-
Reason: One of its dependencies,
HelpWindow.htmlinsrc/main/resources/docsis missing. -
Solution: Execute Gradle task
processResources.
6. Dev Ops
6.1. Build Automation
See UsingGradle.adoc to learn how to use Gradle for build automation.
6.2. Continuous Integration
We use Travis CI and AppVeyor to perform Continuous Integration on our projects. See UsingTravis.adoc and UsingAppVeyor.adoc for more details.
6.3. Coverage Reporting
We use Coveralls to track the code coverage of our projects. See UsingCoveralls.adoc for more details.
6.4. Documentation Previews
When a pull request has changes to asciidoc files, you can use Netlify to see a preview of how the HTML version of those asciidoc files will look like when the pull request is merged. See UsingNetlify.adoc for more details.
6.5. Making a Release
Here are the steps to create a new release.
-
Update the version number in
MainApp.java. -
Generate a JAR file using Gradle.
-
Tag the repo with the version number. e.g.
v0.1 -
Create a new release using GitHub and upload the JAR file you created.
6.6. Managing Dependencies
A project often depends on third-party libraries. For example, Address Book depends on the Jackson library for XML parsing. Managing these dependencies can be automated using Gradle. For example, Gradle can download the dependencies automatically, which is better than these alternatives.
a. Include those libraries in the repo (this bloats the repo size)
b. Require developers to download those libraries manually (this creates extra work for developers)
Appendix A: Suggested Programming Tasks to Get Started
Suggested path for new programmers:
-
First, add small local-impact (i.e. the impact of the change does not go beyond the component) enhancements to one component at a time. Some suggestions are given in Section A.1, “Improving each component”.
-
Next, add a feature that touches multiple components to learn how to implement an end-to-end feature across all components. Section A.2, “Creating a new command:
remark” explains how to go about adding such a feature.
A.1. Improving each component
Each individual exercise in this section is component-based (i.e. you would not need to modify the other components to get it to work).
Logic component
Scenario: You are in charge of logic. During dog-fooding, your team realize that it is troublesome for the user to type the whole command in order to execute a command. Your team devise some strategies to help cut down the amount of typing necessary, and one of the suggestions was to implement aliases for the command words. Your job is to implement such aliases.
Do take a look at Section 2.3, “Logic component” before attempting to modify the Logic component.
|
-
Add a shorthand equivalent alias for each of the individual commands. For example, besides typing
clear, the user can also typecto remove all restaurants in the list.
Model component
Scenario: You are in charge of model. One day, the logic-in-charge approaches you for help. He wants to implement a command such that the user is able to remove a particular tag from everyone in the address book, but the model API does not support such a functionality at the moment. Your job is to implement an API method, so that your teammate can use your API to implement his command.
Do take a look at Section 2.4, “Model component” before attempting to modify the Model component.
|
-
Add a
removeTag(Tag)method. The specified tag will be removed from everyone in the address book.
Ui component
Scenario: You are in charge of ui. During a beta testing session, your team is observing how the users use your address book application. You realize that one of the users occasionally tries to delete non-existent tags from a contact, because the tags all look the same visually, and the user got confused. Another user made a typing mistake in his command, but did not realize he had done so because the error message wasn’t prominent enough. A third user keeps scrolling down the list, because he keeps forgetting the index of the last restaurant in the list. Your job is to implement improvements to the UI to solve all these problems.
Do take a look at Section 2.2, “UI component” before attempting to modify the UI component.
|
-
Use different colors for different tags inside restaurant cards. For example,
friendstags can be all in brown, andcolleaguestags can be all in yellow.Before

After
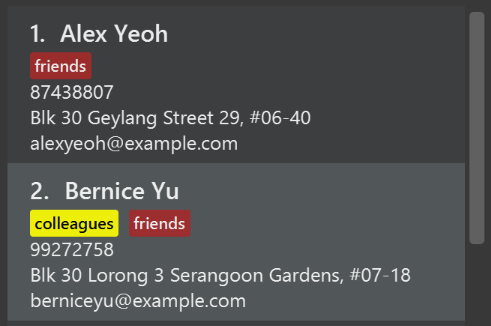
-
Modify
NewResultAvailableEventsuch thatResultDisplaycan show a different style on error (currently it shows the same regardless of errors).Before
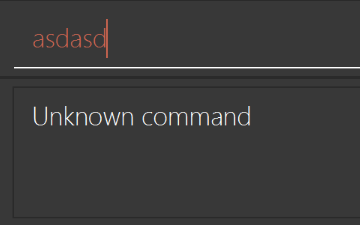
After
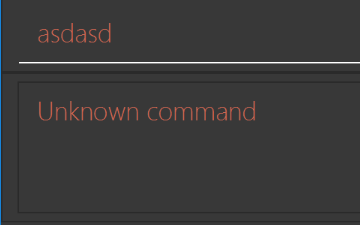
-
Modify the
StatusBarFooterto show the total number of people in the address book.Before

After

Storage component
Scenario: You are in charge of storage. For your next project milestone, your team plans to implement a new feature of saving the address book to the cloud. However, the current implementation of the application constantly saves the address book after the execution of each command, which is not ideal if the user is working on limited internet connection. Your team decided that the application should instead save the changes to a temporary local backup file first, and only upload to the cloud after the user closes the application. Your job is to implement a backup API for the address book storage.
Do take a look at Section 2.5, “Storage component” before attempting to modify the Storage component.
|
-
Add a new method
backupAddressBook(ReadOnlyAddressBook), so that the address book can be saved in a fixed temporary location.
A.2. Creating a new command: remark
By creating this command, you will get a chance to learn how to implement a feature end-to-end, touching all major components of the app.
Scenario: You are a software maintainer for addressbook, as the former developer team has moved on to new projects. The current users of your application have a list of new feature requests that they hope the software will eventually have. The most popular request is to allow adding additional comments/notes about a particular contact, by providing a flexible remark field for each contact, rather than relying on tags alone. After designing the specification for the remark command, you are convinced that this feature is worth implementing. Your job is to implement the remark command.
A.2.1. Description
Edits the remark for a restaurant specified in the INDEX.
Format: remark INDEX r/[REMARK]
Examples:
-
remark 1 r/Likes to drink coffee.
Edits the remark for the first restaurant toLikes to drink coffee. -
remark 1 r/
Removes the remark for the first restaurant.
A.2.2. Step-by-step Instructions
[Step 1] Logic: Teach the app to accept 'remark' which does nothing
Let’s start by teaching the application how to parse a remark command. We will add the logic of remark later.
Main:
-
Add a
RemarkCommandthat extendsCommand. Upon execution, it should just throw anException. -
Modify
AddressBookParserto accept aRemarkCommand.
Tests:
-
Add
RemarkCommandTestthat tests thatexecute()throws an Exception. -
Add new test method to
AddressBookParserTest, which tests that typing "remark" returns an instance ofRemarkCommand.
[Step 2] Logic: Teach the app to accept 'remark' arguments
Let’s teach the application to parse arguments that our remark command will accept. E.g. 1 r/Likes to drink coffee.
Main:
-
Modify
RemarkCommandto take in anIndexandStringand print those two parameters as the error message. -
Add
RemarkCommandParserthat knows how to parse two arguments, one index and one with prefix 'r/'. -
Modify
AddressBookParserto use the newly implementedRemarkCommandParser.
Tests:
-
Modify
RemarkCommandTestto test theRemarkCommand#equals()method. -
Add
RemarkCommandParserTestthat tests different boundary values forRemarkCommandParser. -
Modify
AddressBookParserTestto test that the correct command is generated according to the user input.
[Step 3] Ui: Add a placeholder for remark in RestaurantCard
Let’s add a placeholder on all our RestaurantCard s to display a remark for each restaurant later.
Main:
-
Add a
Labelwith any random text insideRestaurantListCard.fxml. -
Add FXML annotation in
RestaurantCardto tie the variable to the actual label.
Tests:
-
Modify
RestaurantCardHandleso that future tests can read the contents of the remark label.
[Step 4] Model: Add Remark class
We have to properly encapsulate the remark in our Restaurant class. Instead of just using a String, let’s follow the conventional class structure that the codebase already uses by adding a Remark class.
Main:
-
Add
Remarkto model component (you can copy fromAddress, remove the regex and change the names accordingly). -
Modify
RemarkCommandto now take in aRemarkinstead of aString.
Tests:
-
Add test for
Remark, to test theRemark#equals()method.
[Step 5] Model: Modify Restaurant to support a Remark field
Now we have the Remark class, we need to actually use it inside Restaurant.
Main:
-
Add
getRemark()inRestaurant. -
You may assume that the user will not be able to use the
addandeditcommands to modify the remarks field (i.e. the restaurant will be created without a remark). -
Modify
SampleDataUtilto add remarks for the sample data (delete youraddressBook.xmlso that the application will load the sample data when you launch it.)
[Step 6] Storage: Add Remark field to XmlAdaptedRestaurant class
We now have Remark s for Restaurant s, but they will be gone when we exit the application. Let’s modify XmlAdaptedRestaurant to include a Remark field so that it will be saved.
Main:
-
Add a new Xml field for
Remark.
Tests:
-
Fix
invalidAndValidRestaurantAddressBook.xml,typicalRestaurantsAddressBook.xml,validAddressBook.xmletc., such that the XML tests will not fail due to a missing<remark>element.
[Step 6b] Test: Add withRemark() for RestaurantBuilder
Since Restaurant can now have a Remark, we should add a helper method to RestaurantBuilder, so that users are able to create remarks when building a Restaurant.
Tests:
-
Add a new method
withRemark()forRestaurantBuilder. This method will create a newRemarkfor the restaurant that it is currently building. -
Try and use the method on any sample
RestaurantinTypicalRestaurants.
[Step 7] Ui: Connect Remark field to RestaurantCard
Our remark label in RestaurantCard is still a placeholder. Let’s bring it to life by binding it with the actual remark field.
Main:
-
Modify
RestaurantCard's constructor to bind theRemarkfield to theRestaurant's remark.
Tests:
-
Modify
GuiTestAssert#assertCardDisplaysRestaurant(…)so that it will compare the now-functioning remark label.
[Step 8] Logic: Implement RemarkCommand#execute() logic
We now have everything set up… but we still can’t modify the remarks. Let’s finish it up by adding in actual logic for our remark command.
Main:
-
Replace the logic in
RemarkCommand#execute()(that currently just throws anException), with the actual logic to modify the remarks of a restaurant.
Tests:
-
Update
RemarkCommandTestto test that theexecute()logic works.
A.2.3. Full Solution
See this PR for the step-by-step solution.
Appendix B: Product Scope
Target user profile:
-
Diners aiming to find eating places around the National University of Singapore
Value proposition:
With the Makan Book, users can find restaurants based on their preferences such as cuisine or budget. This makes the process of deciding what to eat easier. At the same time, users can give reviews of the restaurants and can view reviews of other users as well. Additionally, Users can add other users as friends and form groups so that they can have private food “Jios”/ sessions. Public food “Jios”, which is open to the whole of NUS, is available as well for the User. Additionally, the User can get recommendations for friends based on mutual friends or others who eat at the same restaurants. Users of the addressbook can also include their own timetable to help them organise jios and eating sessions with friends. Lastly, a user can add restaurants apart from the existing NUS restaurants in their own private Restaurant book. Through the features of the Restaurant Book, we hope the dining experience in NUS can be enhanced.
Feature
Work Division
Evan : Add User Related Features
-
V1.1: Setting up of Storage relating to Users
-
V1.2: Users able to Sign Up, Login and Logout.
-
V1.3: Users able to write reviews for restaurants and view the reviews they’ve written.
Meena :
-
V1.1: Adding of Friendship classes and adding and accepting of friends.
-
V1.2: Deletion of friends and friendRequests.
-
V1.3: Listing of friends and friendRequests.
Chelsea :
-
V1.1: User can create an empty jio with specified parameters.
-
V1.2: Jio stores a list of users, users can delete and join a jio.
-
V1.3: Only the creator can delete a jio. Allow for creation for of group jio. List all jios works with second list panel.
Kate :
-
V1.1: Debt feature related model added.
-
V1.2: User are able to add/delete/accept/clear/list a debt.
-
V1.3: User are able to add debt to a group and auto balancing for debt is implemented. List different type of debt with second list panel.
Yew Woei :
-
V1.1: Timetable feature related models added.
-
V1.2: User can block or free dates. Implemented dates.
-
V1.3: User can list out his schedules for the group.
Appendix C: User Stories
Priorities: High (must have) - * * *, Medium (nice to have) - * *, Low (unlikely to have) - *
| Priority | As a … | I want to … | So that I can… |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Student who hates eating alone |
Find people to eat with or invite people to eat with me |
Not eat alone |
|
Student with many friends |
Create a food jio |
Not have to text all my friends or create a chat group just for eating |
|
Diner |
Be able to write Review for Restaurants |
Let others know what is good and recommended for a more informed decision |
|
Diner |
Be able to view the previous restaurants I’ve been to |
Remember what I have eaten and my experience with the Restaurant |
|
Diner |
Be able to keep track of my favourite restaurants |
Go back to those restaurants |
|
Sociable restaurant |
Add people to my list of friends |
So that they will be in my address book |
|
Sociable restaurant |
Add many friends to a group |
So that we have an exclusive group to start food jios in or keep track of finances |
|
Busy but sociable student |
Have a platform where my timetables can be added |
My friends can find a time to eat with me |
|
Busy but sociable student |
I want to see when my friends are free to eat |
So that i can eat with my friends |
|
Restaurant who always eat as a group |
Know how much should each of us pay |
We can clarify the debt |
|
Restaurant who always eat as a group |
Mark down our payment and balance them off |
Reduce the trouble of paying off each time |
|
Petty friend |
Delete friends |
I can only keep track of friends that I am interested in |
|
user |
View all my friend requests |
I can decide which friend requests to accept and which ones to delete |
|
user |
View all my group requests |
I can decide which group requests to accept and which ones to delete |
|
Diner |
Have outdated jios delete automatically |
Have an updated view of jios |
|
Paranoid restaurant |
Choose to accept or delete friend requests |
I can better protect my privacy |
|
Paranoid restaurant |
Choose which group requests to accept and delete |
I can better protect my privacy |
|
Student who wants to go for jios |
I want to find the jios that fit my timetable |
So that i can easily find a suitable jio without skimming through everything |
|
User |
I want to be able to delete my account and when I want to quit using the app |
Have my Privacy because #Privacy |
|
Restaurant who owes other and is also owed |
Simplify my debts |
Save the hassle of paying and collecting from multiple people |
|
Save the hassle of paying and collecting from multiple people |
Delete groups |
When I view all the activities happening, I can view the groups that I’m interested in |
|
Student who joins a jio |
Be able to suggest alternative timings/places etc |
Fit my timetable better |
|
Selective friend |
Create private jios for only my friends |
Have a private meal |
|
Sociable restaurant |
Get recommendations for friends based on mutual friends |
So that I can have more friends |
|
Time-strapped student |
I want to add my times tables easily using google docs integration |
So that i can easily find a common time slot with friends |
|
Time-strapped student |
I want to add my times tables easily using nusmods integration |
So that i can easily find a common time slot with friends |
|
Diner |
Be able to send recommendations on certain restaurants |
Notify my friends where I have eaten at |
|
Diner |
Keep track of visited restaurants outside of NUS |
Have more variety in the restaurant choices |
|
Financially strapped student |
Set the address book to sort the restaurant by budget |
Find the restaurant that I can avoid |
|
Busy diner that travels around |
Sort by faculty |
Eat where I am heading to |
|
Time-strapped student |
Have my filter settings saved |
Save time from applying the same filter each time |
|
Vegetarian diner |
Set the address book to always eliminate the non-veg restaurant |
Always find the restaurant provides vegetarian food |
|
Boutique food lover |
Use the address book to find relevant restaurants for me |
Easily find a restaurant suits my taste like Chinese, Western, Malay, Indian, Korean, Japanese, Vietnamese, Others |
Appendix D: Use Cases
(For all use cases below, the System is the Makan Book and the Actor is the user, unless specified otherwise)
Use case #1: Meeting with friends to eat together at a place in NUS
System: Food Jio system
Actor: User, friends
MSS
-
User creates a jio with a unique name and specifies the time, date, place to meet.
-
System adds jio to public list of jios.
-
Friend views the public list of all jios.
-
Friend joins a jio.
-
Jio is deleted when jio is over.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. System detects an error in the entered data.
-
1a1. System displays error message.
Use case ends.
-
-
1a. System detects an error in the entered data.
-
1a1. System displays error message.
Use case ends.
-
-
3a. User requests for the jio to be private
-
3a1. Jio is only visible to friends of the user who added.
-
3a2. Friend view the private list of jios on top of the public list of jios.
Use case resumes from step 4.
-
Use case #2: Adding a Review to a Restaurant Visited
System: Restaurant review system
Actor: User
MSS
-
User eats at a Restaurant and finds the restaurant (with List/Find function) in NUS
-
System returns the list of Restaurants for User to choose from
-
User chooses the restaurant using the index and writes a review for the particular restaurant that he has chosen
-
System checks whether review is valid
-
System adds the review to the restaurant
Extensions:
-
4a. System detects an error in the entered data.
-
4a1. System displays a message on how the command should be used
Use case ends.
-
Use case #3: Adding friends and groups
System: Friend and group system
Actor: User, friends
MSS 1. User adds friend or different users to a group with a unique name. 2. Other user can view all requests made to him. 3. Other user in question chooses whether to accept or delete the request. 4. The other user chooses to accept the request, they will now have a friendship or be added to the group. 5. User can view all friends and groups through a list.
Extensions:
-
1a. System detects an error in the entered data.
-
1a1. System displays a message on how the command should be used
Use case ends.
-
-
3a. System detects an error in the entered data.
-
3a1. System displays a message on how the command should be used
Use case ends.
-
-
4a. Other user chooses to delete request.
-
4a1. The other user will not have a friendship or be added to the group.
Use case resumes from step 5.
-
Use case #4: Finding a common timeslot to eat with friends
System: Timetable system
Actor: User
MSS 1. Student blocks out unavailable times and dates. 2. Timetable System blocks out the date and prints an OK status. 3. Step 1-2 are repeated until student sets up his timetable system. 4. Student requests to find a common timeslot for eating with friend 5. Timetable System finds the common free times across all the friend’s schedules and displays to user.
Extensions:
-
1a. System detects an error in the entered data.
-
1a1. System displays a message on how the command should be used
Use case ends.
-
Use case #5: Settling payment for a group meal
System: Payment splitting system
Actor: User, friends
MSS 1. User creates a debt request to the whole group, with the total meal fee. 2. System splits the fee into equal amounts 3. System sends a debt request to every other member in the group. 4. Debtor accepts the debt request. 5. A debt record is created to both debtor and creditor. 6. After the debt is paid, debtor creates a clear request to user. 7. System sends clear request to user. 8. User accepts clear request. 9. System records that the debt is paid.
Extensions:
-
4a. Debtor rejects the request.
-
4a1. Debt request is deleted.
-
4a2. System sends notification to the request sender.
Use case ends.
-
-
8a. User rejects the request.
-
11a1. Clear request is deleted.
-
11a2. System sends notification to the request sender.
Use case ends.
-
Appendix E: Non Functional Requirements
-
Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java
9or higher installed. -
Should be able to hold up to 1000 restaurants without a noticeable sluggishness in performance for typical usage.
-
A user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
-
It is not secure as there is no encryption of password when storing them
-
Application and stored data is only available on one computer. The different users have to use the same application on the same computer.
{More to be added}
Appendix G: Instructions for Manual Testing
Given below are instructions to test the app manually.
| These instructions only provide a starting point for testers to work on; testers are expected to do more exploratory testing. |
G.1. Launch and Shutdown
-
Initial launch
-
Download the jar file and copy into an empty folder
-
Double-click the jar file
Expected: Shows the GUI with a set of sample contacts. The window size may not be optimum.
-
-
Saving window preferences
-
Resize the window to an optimum size. Move the window to a different location. Close the window.
-
Re-launch the app by double-clicking the jar file.
Expected: The most recent window size and location is retained. === Sign Up for Makan Book
-
-
Signing Up for an Account in the Makan Book.
-
Prerequisites: User does not have an existing account in the Makan Book.
-
Test case:
signup u/johnnydoe pwd/pAssw0rd n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com
Expected: Successfully Registered
-
-
-
logoutand Sign Up with the same username as before-
Prerequisites: Username is already taken in Makan Book.
-
Test case:
signup u/johnnydoe pwd/pAssw0rd n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com
Expected: This username already exists in the Makan Book
-
-
G.2. Login a User
-
Log in into an non-existing Makan Book Account.
-
Prerequisites: User does not have an account in the Makan Book.
-
Test case:
login u/naveko pwd/asd
Expected: Either Username or Password is Incorrect
-
-
-
Log in into an existing Makan Book Account, but with incorrect password.
-
Prerequisites: User has an existing account, log in with incorrect password.
-
Test case:
login u/johnnydoe pwd/password
Expected: Either Username or Password is Incorrect
-
-
-
Log in into an existing Makan Book Account, with correct password.
-
Prerequisites: User has an existing account and is currently not logged in.
-
Test case:
login u/johnnydoe pwd/pAssw0rd
Expected: Successfully Logged In
-
-
-
Log in again while in an existing session.
-
Prerequisites: User is currently logged in and tries to log in again.
-
Test case:
login u/johnnydoe pwd/pAssw0rd
Expected: User is already logged in
-
-
G.3. Log Out a User
-
Log Out from an existing session.
-
Prerequisites: User is currently logged in.
-
Test case:
logout
Expected: Successfully Logged Out
-
-
-
Log Out again despite no active session.
-
Prerequisites: Log out even though no user is currently logged in.
-
Test case:
logout
Expected: There is no user currently logged in
-
-
G.4. Display Current User Profile
-
Login into an account and enter
displayProfile.-
Prerequisites: User is currently logged in.
-
Test case:
displayProfile
Expected: Displaying User Profile
-
-
-
Logout and enter
displayProfile.-
Prerequisites: Display Profile Command used despite having no current User logged in.
-
Test case:
displayProfile
Expected: User is not currently logged in
-
-
G.5. Write a Review
-
Login into an account and write a proper review
-
Prerequisites: User is currently logged in and review is in the proper format.
-
Test case:
writeReview 1 rate/3 rvw/The cold noodles and pork bulgogi were delicious.
Expected: Successfully Wrote Review
-
-
-
Login into an account and Write an incorrect review with incorrect rating
-
Prerequisites: User is currently logged in and rating given is not from 1 to 5.
-
Test case:
writeReview 1 rate/6 rvw/The cold noodles and pork bulgogi were delicious.
Expected: Rating must be a positive integer from 1 to 5 where 1 is the lowest rating and 5, the highest rating.
-
-
-
Login into an account and Write an incorrect review with blank review
-
Prerequisites: User is currently logged in and written review is empty.
-
Test case:
writeReview 1 rate/5 rvw/
Expected: Written Reviews can take any values, and it should not be blank.
-
-
G.6. Saving data
-
Dealing with missing/corrupted data files
-
Corrupted Xml: The application will start with an empty addressbook.xml and users.xml.
-
Missing Xml: The application would generate sample addressbook.xml and users.xml and store it in the data folder
-
G.7. Adding friends
-
Add a valid user as a friend
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as meena567. meena567 is not already friends and has not sent a friend request to katespades
-
Test case:
addFriend u/katespades
Expected: Friend request sent to: katespades
-
-
-
Send a friend request to a user multiple times
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as meena567. Have already sent a friend request previously to katespades which has not been accepted or deleted by katespades
-
Test case:
addFriend u/katespades
Expected: You have already sent friend request to this User
-
-
-
Send a friend request to a user who has sent a friend request to you previously
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as meena567. meena567 has a friend request from katespades which has not been accepted yet by meena567.
-
Test case:
addFriend u/katespades
Expected: You have that user’s friend request. Please accept that request instead of adding them as a friend.
-
-
-
Send a friend request to a user who is already a friend
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as meena567. meena567 is already friends with katespades.
-
Test case:
addFriend u/katespades
Expected: You are already friends with this user.
-
-
G.8. Accepting friends
-
Accepting a valid friend request
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as meena567. meena567 has a friend request from katespades
-
Test case:
acceptFriend u/katespades
Expected: Successfully accepted friend request of: katespades
-
-
-
Accepting an invalid friend request
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as meena567. meena567 does not have a friend request from katespades
-
Test case:
acceptFriend u/katespades
Expected: Sorry, that user is not in your friend requests' list.
-
-
G.9. Deleting friend requests
-
Deleting a valid friend request
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as meena567. meena567 has a friend request from katespades
-
Test case:
deleteFriendRequest u/katespades
Expected: Successfully deleted friend request of user : katespades
-
-
-
Deleting an invalid friend request
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as meena567. meena567 does not have a friend request from katespades
-
Test case:
deleteFriendRequest u/katespades
Expected: Sorry, that User did not send you a friend request.
-
-
G.10. Deleting friends
-
Deleting a valid friend
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as meena567. meena567 is friends with katespades
-
Test case:
deleteFriend u/katespades
Expected: Successfully deleted friend with username: katespades
-
-
-
Deleting an invalid friend request
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as meena567. meena567 is not friends with katespades
-
Test case:
deleteFriend u/katespades
Expected: Sorry, the friend that you want to delete does not exist in your list of friends
-
-
G.11. Adding groups
-
Adding a valid group
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as meena567 and wants to add a group with name CS2103. CS2103 is not the name of any other group in Makan Book.
-
Test case:
addGroup g/CS2103
Expected: Group created: CS2103
-
-
-
Adding an invalid group
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as meena567 and wants to add a group with name CS2103. However, there exists another group with name CS2103.
-
Test case:
addGroup u/CS2103
Expected: Sorry, a group with that name exists. Please choose a different group name.
-
-
G.12. Accepting groups
-
Accepting a valid group request
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as meena567. meena567 has a group request from CS2103
-
Test case:
acceptGroup g/CS2103
Expected: Successfully accepted group request of: CS2103
-
-
-
Accepting an invalid group request
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as meena567. meena567 does not have a group request from CS2103
-
Test case:
acceptGroup g/CS2103
Expected: Sorry, that group is not in your group requests' list.
-
-
G.13. Adding members to groups
-
Adding all valid members
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as meena567 and meena567 is part of group CS2103. meena567 wants to add users who are not part of the group and have previously received group request.
-
Test case:
addMembers g/CS2103 u/katespades u/thejrlinguist
Expected: Members added to group: CS2103=[katespades, thejrlinguist]
-
-
-
Adding some members who are part of the group
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as meena567 and meena567 is part of group CS2103. meena567 wants to add users thejrlinguist and katespades to the group. However, thejrlinguist is already part of the group but katespades is not.
-
Test case:
addMembers g/CS2103 u/katespades u/thejrlinguist
Expected: Sorry, username to be added is in the group. No users were added to the group.-
Even though katespades is not a part of the group, the command will not add any members to the group as thejrlinguist is already inside the group.
-
-
-
-
Adding users who already have a group request
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as meena567 and meena567 is part of group CS2103. meena567 wants to add katespades to the group. However, katespades already has a request to the group.
-
Test case:
addMembers g/CS2103 u/katespades
Expected: Sorry, User already has a request for that group.
-
-
G.14. Deleting group requests
-
Deleting a valid group request
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as meena567. meena567 has a group request from CS2103
-
Test case:
deleteGroupRequest g/CS2103
Expected: Successfully deleted group request of group : CS2103
-
-
-
Deleting an invalid group request
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as meena567. meena567 does not have a group request from CS2103
-
Test case:
deleteGroupRequest g/CS2103
Expected: Sorry, you do not have that group request
-
-
G.15. Deleting group
-
Deleting a valid group
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as meena567. meena567 is part of CS2103 group
-
Test case:
deleteGroup g/CS2103
Expected: Successfully deleted group with name: CS2103
-
-
-
Deleting an invalid group
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as meena567. meena567 is not in CS2103 group
-
Test case:
deleteGroup g/CS2103
Expected: Sorry, the group that you want to delete does not exist in your list of groups
-
-
G.16. Create a jio
-
Create a jio with vaild parameters
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as chelchia. A jio of the same name has not already been created
-
Test case:
createJio n/manualtestjio w/1 d/mon h/1200 a/FineFood
Expected: New jio added: manualtestjio Date: [NUS Week: 1 Day:mon Time:1200] Address: FineFood People: chelchia
-
-
-
Create a group jio with valid parameter
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in as chelchia. A group 2103 exists
-
Test case:
createJio n/groupjio w/1 d/mon h/1200 a/FineFood g/2103
Expected: New jio added: groupjio Date: [NUS Week: 1 Day:mon Time:1200] Address: FineFood People: chelchia navekom meena567 aiden katespades
-
-
-
Create a jio with same jio name
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in.
-
Test case:
createJio n/manualtestjio w/1 d/mon h/1200 a/FineFood
Expected: A jio with the same name already exists
-
-
G.17. Join a jio
-
Join a valid jio
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in. User is not creator of jio.
-
Test case:
joinJio n/manualtestjio
Expected: Jio joined: manualtestjio
-
-
-
Join a non-existent jio
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in.
-
Test case:
joinJio n/randomjio
Expected: This jio does not exist
-
-
G.18. Delete jio
-
Delete a valid jio user created
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in. User is creator of jio.
-
Test case:
deleteJio n/manualtestjio
Expected: Jio deleted: manualtestjio
-
-
-
Delete a valid jio not created by user
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in. User is not creator of jio.
-
Test case:
deleteJio n/manualtestjio
Expected: You are not the creator of this jio. Only the creator can delete a jio.
-
-
-
Join a non-existent jio
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in.
-
Test case:
deleteJio n/randomjio
Expected: Jio does not exist.
-
-
G.19. Block Date from your schedule.
-
Block a valid date from your schedule
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in. The date is not blocked on your schedule.
-
Test case:
blockDate w/recess d/mon h/1800
Expected: New date added on your schedule: [NUS Week: recess Day:mon Time:1800].
-
-
-
Block a valid date that is already on your schedule
-
Block a valid date from your schedule
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in. The date is blocked on your schedule.
-
Test case:
blockDate w/recess d/mon h/1800
Expected: This busy date already exists in your schedule.
-
-
G.20. Free Date from your schedule.
-
Free a valid date from your schedule
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in. The date is blocked on your schedule.
-
Test case:
freeDate w/recess d/mon h/1800
Expected: Time has been unblocked on your schedule: [NUS Week: recess Day:mon Time:1800]
-
-
-
Free a valid date from your schedule when it is already free.
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in. The date is blocked on your schedule.
-
Test case:
freeDate w/recess d/mon h/1800
Expected: This time block is already free on your schedule.
-
-
G.21. List your schedule for the week.
-
List your schedule for a valid week.
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in.
-
Test case:
listScheduleForWeek w/13
Expected: Your schedule will be listed in the browser panel as a html document with the heading: These are your free dates for the Week: 13.
-
-
G.22. Find free timeslots to meet among your group members for a week.
-
Find free timeslots to meet among group members for a valid group and a valid week.
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in and part of a group.
-
Test case:
findDates g/2103 w/13
Expected: The list of timeslots for meeting will be listed in the browser panel as a html document with the heading: These are the common free dates for Group: 2103 on Week: 13.
-
-
-
Find free timeslots to meet among group members for a invalid group and a valid week.
-
Prerequisites: User is logged in and not part of the group.
-
Test case:
findDates g/krustycrab w/13
Expected: You are not in that group.
-
-
G.23. Add Debt
-
Prerequisites:
-
User is logged in.
-
Input debtor name should correspond to a valid user.
-
Input amount should be larger than zero, less than a hundred million and less than two decimal places.
-
Add Debt to a valid user with valid amount
-
Test case:
addDebt u/katespades amt/12
Expected: A debt request of 12.000000 SGD to katespades is sent
-
-
Add Debt to a invalid user with valid amount
-
Test case:
addDebt u/test123 amt/12
Expected: Input user not exist.
-
-
Add debt to a valid user with invalid amount
-
Test case:
addDebt u/katespades amt/99999999999
Expected: Input amount must be larger than zero and less than a hundred million.
-
-
-
G.24. Add Group Debt
-
Prerequisites:
-
User is logged in.
-
Input group name should correspond to a valid group.
-
User is a accepted user for the correspond input group.
-
Input amount should be larger than zero, less than a hundred million and less than two decimal places.
-
Add debt to a valid group with valid amount
-
Test case:
addGroupDebt g/2103 amt/12
Expected: A debt request of 12.000000 SGD to other member in 2103 is sent
-
-
-
G.25. Accept Debt Request
-
Prerequisites:
-
User is logged in.
-
Input creditor name should correspond to a valid user.
-
A
PENDINGdebt exist between user(as a debtor) and input creditor, with amount and debt id match the input amount and debt id.
-
-
Accept a debt request received
-
Test case:
acceptDebtRequest u/meena567 amt/12 id/18111216484190
Expected: Debt request(ID: 18111216484190) from meena567 of 12.000000 SGD has been accepted.
-
-
Accept a non-existent debt request received
-
Test case:
acceptDebtRequest u/meena567 amt/18 id/110111216482190(random id and amount)
Expected: Input debt not exist.
-
G.26. Delete Debt Request
-
Prerequisites:
-
User is logged in.
-
Input creditor name should correspond to a valid user.
-
A
PENDINGdebt exist between user(as a debtor) and input creditor, with amount and debt id match the input amount and debt id.
-
-
Delete a debt request received
-
Test case:
deleteDebtRequest u/meena567 amt/12 id/18111216484190
Expected: Debt request(ID: 181112172248904) from meena567 of 3.000000 SGD has been deleted.
-
-
Delete a non-existent debt request received
-
Test case:
deleteDebtRequest u/meena567 amt/18 id/110111216482190(random id and amount)
Expected: Input debt not exist.
-
G.27. Clear Debt
-
Prerequisites:
-
User is logged in.
-
Input debtor name should correspond to a valid user.
-
An
ACCEPTEDexist between user(as a creditor) and input debtor. -
Input amount should be larger than zero, less than the amount of corresponding debt.
-
Clear Debt to a valid user with valid amount
-
Test case:
clearDebt u/katespades amt/7
Expected: katespades’s debt of 7.000000 SGD is cleared.
-
-
Clear Debt to a invalid user(not your debtor) with valid amount
-
Test case:
clearDebt u/chelchia amt/3
Expected: There are no debt between you and input user
-
-
Add debt to a valid user with invalid amount
-
Test case:
clearDebt u/katespades amt/0
Expected: Input amount should be larger than zero.
-
-
-